1. Types of Sedation:
Nitrous Oxide (Laughing Gas): This is a mild form of sedation administered through a mask over the nose. It helps children relax and reduces anxiety during dental procedures. Nitrous oxide wears off quickly, allowing the child to resume their normal activities after the procedure.
Oral Sedation: This involves giving the child a prescribed medication (in liquid form) to be taken before the procedure. Oral sedation induces relaxation and drowsiness, but the child remains awake and responsive. The child may remember little to nothing about the procedure.
2. Reasons for Sedation:
- Dental Anxiety: Many children experience dental anxiety or fear of dental procedures. Sedation helps alleviate this anxiety, making the experience more comfortable.
- Complex Procedures: Sedation is often used for complex procedures or treatments that may be uncomfortable or time-consuming.
- Young Age: Young children who may have difficulty cooperating during procedures can benefit from sedation to ensure their safety and comfort.
- Special Needs: Children with special needs may require sedation to complete dental procedures safely and effectively.
3. Safety and Monitoring:
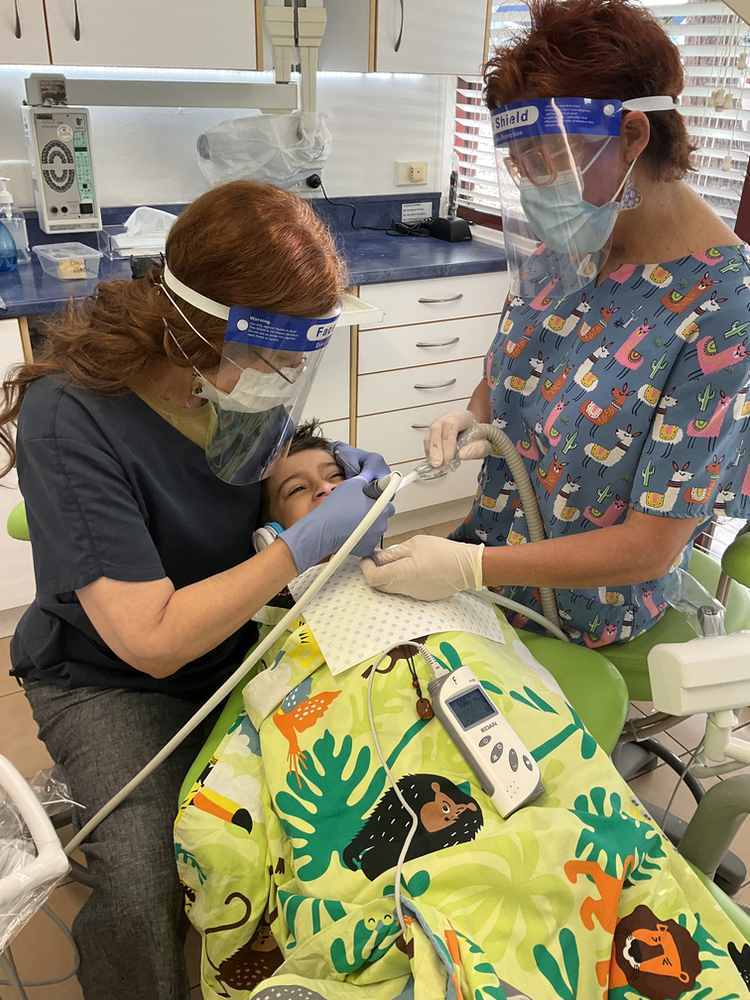
Before sedation, a thorough medical history is obtained to ensure the child is a suitable candidate. The child is monitored visually and using a pulse oximeter. Monitoring continues during and after the procedure until the child is alert and stable.
The child must be fasted from food and drinks. Fasting time is dependent on the type of sedation used.
Dental sedation for children is conducted under strict safety protocols. A trained dental team, including a specialist paediatric dentist and staff of well-trained dental assistants monitor the child's vital signs throughout the procedure.
4. Parental Involvement:
Parents or guardians play an important role in the sedation process. They provide information about the child's medical history and are required to accompany the child to the appointment.
5. Post-Sedation Care:
After the procedure, children are monitored until they are fully awake and responsive. Parents receive post-sedation care instructions, including what the child can eat and drink. Followed by post operative communications.
6. Communication:
Effective communication between the dental team and parents is crucial. Parents should inform the dental team about any allergies, medications, or health conditions the child may have.
Dental sedation for children can be a valuable tool in providing safe and comfortable dental care. If you're considering sedation for your child, discuss your concerns with our qualified paediatric dentist. Dr Hadi can help you understand the options, risks, and benefits, and ensure that your child's dental experience is positive and stress-free.